Hi everyone. How are you guys? I hope you guys are doing fine.
The topic for today's class is CABLING.
Cable is the medium through which information usually moves from one network device to another. Several types of cable are commonly used with LANs. In some cases, a network will utilize only one type of cable, other networks will use a variety of cable types.
CABLING
GUIDED = BOUNDED
UNBOUNDED = UNGUIDED
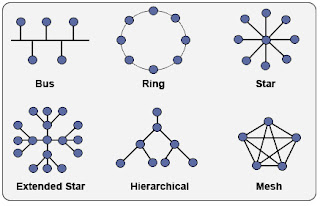
Types of Cables
1) Twisted-Pair Cable
A twisted pair consists of two insulated copper wires, typically about 1 mm thickness. The wires are twisted together in a helical shape. The purpose of twisting the wires is to reduce electrical interference from similar pairs that are close by.
Twisted pair wires are commonly used in local telephone communication and for digital data transmission over short distances up to 1 km. When many twisted pairs run in parallel for a substantial distance, such as all the wires coming from a multistory apartment building to the telephone exchange, they are bundled together and placed in a protective sheath. The pairs in these bundles would interfere with one another if they are not twisted.
Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) Cable
Advantages of Twisted-Pair Wire
- Being the oldest method of data transmission, trained manpower to repair and service this media of communications are easily available.
- In a telephone system, signals can travel several kilometers without amplification when twisted pair wires are used.
- These media can be used for both analog and digital data transmission. The bandwidth depends on the thickness of the wire and the distance traveled, but several megabits per second can be achieved for a few kilometers in may cases.
- It is the least expensive media for transmission for short distances.
- If a portion of a twisted-pair cable is damaged, the entire network is not shut down as it may be the case with coaxial cable.
Disadvantages of UTP Cable
- Easily pick up noise signals which results in higher error rates when the line length exceeds 100 meters.
- Being this in size, it is likely to break easily.
- It can support 19,200 bps up to 50 feet on RS-232 port.
Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) Cable
Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) has a grounded outer copper shield around the bundle of twisted pairs or around each pair.This provide added protection against Electromagnetic Interference (EMI).
Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) does not have a grounded copper shield. UTP cables are easier to work with and are less expensive than shielded cables.
Shielded wire is used in an electricity noisy environment to limit the effects of noise absorption. Twisted-pair wiring is more commonly used for LAN media.
The unique thing about twisted pair network cabling is the fact that the wires are twisted. This is done because we run an electrical current through a piece of copper wiring, Electromagnetic Interference and cross talk around the wires. That can be a problem when we have a second wire in close proximity because it can absorb the signal from the first wire. In that case the data on wires can get corrupted.
2) Coaxial Cable
A coaxial cable is one that consists of two conductors that share a common axis. The inner conductor is typically a straight wire,either solid or stranded and the outer conductor is typically a shield that might be braided or a foil. Coaxial cable is a cable type used to carry radio signals, video signals, measurement signals and data signals. Most common coaxial cable impedances in use in various applications are 50 ohms and 75 ohms.
Advantages of Coaxial Cable
- It has better shield against electromagnetic interference than twisted pair cable, so it can span longer distance a t higher data bits per second (bps).
- It can be used for both analog and digital data transmissions. For analog g data transmission, 75-ohm broadband coaxial is used and for digital transmission, 50 - ohm base band cable is used.
- It is inexpensive as compared to twisted pair wires and UTP cables but easy to handle.
3) Fiber Optic Cable
Optic Fiber is the newest form of bounded media. This media is superior in data handling and security characteristics. The fiber optic cable transmits light signals rather than electrical signals. It is far more efficient that the other network transmission media. Each fiber has an inner core of glass or plastic that conducts light. There are two types of light sources for which fiber cables are available. These sources of light are:
a. Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs)
b. Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission Radiation (Lasers)
Below figure shows the principle of operation of the fiber optic system. The system basically consists of fiber optic cables that are made of tiny threads of glass or plastics. In a single- mode fiber, the core is 8 to 10 microns ( about the size of hair). In multimode, the core is about 50 microns on diameter.
Advantages of Fiber Optic Cable
- It can handle much higher bandwidth than copper. Due to the low attenuation, repeaters are needed only about every 30 km on fiber lines, versus about every 5 km for copper.
- Fiber is not affected by power surges, electromagnetic interference, or power failure. Nor is it affected by corrosive chemicals in the air, making it ideal for factory environments where electrical interference is very high.
- Fiber is lighter than copper. One thousand twisted pairs copper cables of 1 km long weigh 800 kg. But fibers have only 100 kg.
- Fibers do not leak light and are quite difficult to tap. This gives them excellent security against potential wire-tappers.
Disadvantages of Fiber Optic Cable
- Fiber is an unfamiliar technology requiring skills which may not be easily available.
- Since optical transmission is inherently unidirectional, two-way communication requires either two fiber cables or two frequency bands on one fiber.
- Fiber interfaces cost more than electrical interfaces.
4) Wireless LANs
A wireless LAN (or WLAN, for wireless local area network, sometimes referred to as LAWN, for local area wireless network) is one in which a mobile user can connect to a local area network (LAN) through a wireless (radio) connection. The IEEE 802.11 standards use the Ethernet Protocol and CSMA/CA (carrier sense multiple access with collision avoidance) for path sharing and include an encryption method, the Wired Equivalent Privacy Algorithm.
That is all for this week. Thank you for reading my entry.





+Aerial+Fiber+Optic+Cable.gif)