
Hi everyone. The topic for today's class is TOPOLOGY.
Network Topology is the study of the arrangement or mapping of the elements (links,nodes) of a network. It is divided into two which are the physical (real) andlogical (virtual) interconnections between nodes.
PHYSICAL TOPOLOGY
The physical layout of devices on a network.
The way that the devices on a network are arranged and how they communicate with each other.
The workstations are connected to the network through the actual cables that transmit data.
The physical structure of the network.
LOGICAL TOPOLOGY
The mapping of the flow of data between the nodes in the network determines the logical topology of the network.
The way that the signals act on the network media.
The way that the data passes through the network from one device to the next without regard to the physical in interconnection of the devices.
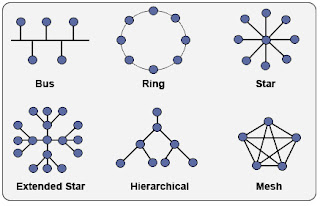
CLASSIFICATION OF PHYSICAL TOPOLOGY
Linear bus
Star
Star- Wired Ring
Tree
FDDI
Mesh
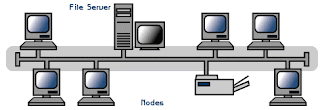
LINEAR BUS
consists of a main run of cable with a terminator at each end.
all nodes ( file server, workstations and peripherals) are connected to the linear cable.
Ethernet and Local Talk networks use a linear bus topology.
Advantages of a Linear Bus Topology:
Easy to connect a computer or peripheral to a linear bus.
Requires less cable length than a star topology.
Disadvantages:
Entire network shuts down if there is a break in the main cable.
A faulty cable or workstation will take the entire LAN down.
Terminators are required at both ends of the backbone cable.
Difficult to identify the problem if the entire network shuts down.
Not meant to be used as a stand- alone solution in a large building.
Summary:
Advantages of Linear Bus
Easy to install
Costs are usually low
Easy to add systems to network
Great for small networks
Disadvantages of Linear Bus
Out-of-date technology
If cable breaks, whole network is down
Can be difficult to troubleshoot
Unmanageable in a large network
RING
each of the systems is connected to its respective neighbor forming a ring.
the main difference between the bus and the ring is that the ring topology does not require termination. Because the systems are connected all together in a loop.
there is no beginning and end point as there is with the bus topology.
this configuration is seen in Fiber Distributes Data Interface (FDDI) networks.
Advantages of RING:
easy to install
costs are usually low
easy to add systems to network
great for small networks
Disadvantages of RING:
out-of-date technology
if cable breaks, whole network is down
can be difficult to troubleshoot
unmanageable in a large network
STAR
A star topology is designed with each node (file server, workstations and peripherals) connected directly to a central network hub or connector.
Data on a star network passes through the hub manages and controls all function of the network.
It also acts as a repeater for the data flow.
This configuration is common with twisted pair cable; however, it can also be used with coaxial cable or fiber optic cable.
The protocols used with star configurations are usually Ethernet or Local Talk.
Advantages of Star:
easy to install and wire
easy to add new workstations
no disruptions to the network when connecting or removing devices
any non-centralized failure will have very little effect on the network
easy to detect faults and to remove parts.
centralized control
centralized network/hub monitoring
Disadvantages of Star:
Requires more cable length than a linear topology.
If the hub or connector fails, nodes attached are disabled.
More expensive than linear bus topology because of the cost of the hub.
STAR-WIRED
A star wired topology may appear (externally) to be the same as a star topology.
Internally, the Multistation Access Unit (MAU) of a star wired ring contains wiring that allows information to pass from one device to another in a circle or ring.
The Token Ring protocol uses a star-wired topology.
TREE
A Tree (hybrid) topology combines characteristics of linear bus and star topology.
It consists of groups of star-configured workstations connected to a linear bus backbones cable.
Tree topology allow for the expansion of an existing network, and enable schools to configure a network to meet their needs.
Advantages of Tree:
Point-to-point writing for individual segments.
Disadvantages of Tree:
Overall length of each segment is limited by the type of cabling used.
If the backbone line breaks, the entire segment goes down.
More difficult to configure and wire than the other topology.
FDDI
100 mbps
Normally implemented over fiber optic (fast-Ethernet, UTP)
Dual redundancy built in by use of primary and secondary ring.
Automatic by passing and isolation of faulty nodes.
LAN PROTOCOLS
ETHERNET
TOKEN RING
FDDI
GIGABIT ETHERNET
PROTOCOL
A protocol is a set of rules that governs the communications between computers on a network.
These rules include guidelines that regulate the following characteristics of a network:
- access method
- allowed physical topology
- cables of cabling
- speed of data transfer
Logical topology are bound to network protocols and describe how data is moved across the network.
The Ethernet protocol is a common logical bus topology protocol.
Local Talk is a common logical bus or star topology protocol.
Token Ring is a common logical ring topology protocol.
CABLING
Cable is the medium through which information usually moves from one network device to another.
Several types of cable are commonly used with LANs.
In some cases, a network will utilize only one type of cable, other networks will use a variety of cable types.
TYPES OF CABLES
Non-shielded Twisted Pair (UTP) Cable
Shielded Twisted Pair (UTP) Cable
Coaxial Cable
Fiber Optic Cable
Wireless LANs
That is all for this week lesson. Thank you.




No comments:
Post a Comment