


Hi everyone. Topic for today's lesson is Introduction to Networking. There are a few discussion for this topic. There are:
1- Introduction to Computer Networking
2 - The Importance of Networking
3 - Data Communication
4 - Introduction to Networking Devices/Equipment
5- Introduction to Networking Software
Computer Networking
A collection of hardware components and computers interconnected by communication channels that allow sharing of resources and information.
Networking Component
Terminal, Workstations, Computers
Transmission Media
Network Electronics
Software
Network Architecture Standards
LAN = Local Area Network
Typical LAN configuration : one computer as a server
To store all of the software that controls the network and to share by all the computers attached to the network.
Cable connects to the server.
WAN = Wide Area Network
This kind of network is complicated. It uses multiplexing to connect the local and metropolitan network called hybrid network.
MAN = Metropolitan Area Network
A computer network that usually spans a city or a large campus. A MAN usually interconnects a number of local area networks (LANs) using a high-capacity backbone technology, such as fiber-optical links, and provides up-link services to wide area networks (or WAN) and the Internet. Similar to a LAN but typically over a larger area like a city.
PAN = Personal Area Network
* A network used to connect wireless devices (such as Bluetooth-enabled devices)
in close proximity to each other.
* An emerging technology that uses wireless communication to exchange data
between computing devices using short-range radio communication, typically
within an area of 10 meters.
* A computer network that supports wireless connections within a room or small area.
Server
Multiplexing
Multiplexing is sending multiple signals or streams of information on a carrier at the same time in the form of a single, complex signal and then recovering the separate signals at the receiving end.
Hybrid Network
Hybrid networks use a combination of any two or more topologies in such a way that the resulting network does not exhibit one of the standard topologies. A hybrid topology is always produced when two different basic network topologies are connected. Two common examples for Hybrid network are: star ring network and star bus network.
Network Categorized
Topology (geometric arrangement of the network)
Protocol (common set of rules and signals the computers on the network use to communicate)
Architecture (peer to peer/client/server)
Bounded media
The physical links through which signals are confined to narrow path. Bounded media are made up of a external conductor(usually copper) bounded by jacket material. These are also called guided media.
Unbounded media
No physical connection is required. Space or air is the transmission medium for electromagnetic waves. Source and destination can be static or mobile. Broad spectrum from low to high bandwidth is available. Can be quickly implemented.
NETWORK ELECTRONIC DEVICES
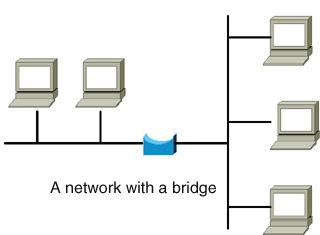
Bridge
A Bridge does just what you would expect it to do - it joins two networks together so as far as data packets are concerned it looks like one large network. A bridge is not as capable as a Router - but it is less expensive.
Routers
A Router is a device that transfers data from one network to another in an intelligent way. It has the task of forwarding data packets to their destination by the most efficient route. In order to do this, the router has a micro computer inside it. This holds a table in memory that contains a list of all the networks it is connected to, along with the latest information on how busy each path in the network is, at that moment. This is called the 'routing table'. When a data packet arrives, the router does the following:-
 | Reads the data packet's destination address |
 | Looks up all the paths it has available to get to that address. |
 | Checks on how busy each path is at the moment |
 | Sends the packet along the least congested (fastest) path. |

Hub
The network 'Hub' allows computers to share data packets within a network.

Each computer will be connected to a single 'port' on the hub. So if you purchase an '8 port hub', you will be able to connect up to eight computers together.
You can also 'daisy chain' hubs to allow even more computers to join the network.

Gateways
A gateway converts the data passing between dissimilar networks so that each side can communicate with each other. i.e converts data into the correct network protocol.
The gateway is a mixture of hardware components and software.
This is unlike a standard 'Bridge' which simply joins two networks together that share the same protocol.

My opinion:


 In my opinion, networking really helpful in our daily life. It makes us easy to connect with other people. Other than that, it benefits us in terms of works. The main thing is that it is very exciting to explore networking. There are too many tools that I do not know. I use it but i do not know the exact name of the tools. It is such a waste if I do not grab this knowledge.
In my opinion, networking really helpful in our daily life. It makes us easy to connect with other people. Other than that, it benefits us in terms of works. The main thing is that it is very exciting to explore networking. There are too many tools that I do not know. I use it but i do not know the exact name of the tools. It is such a waste if I do not grab this knowledge.
That is all for today's lesson. I'll continue next week.










 In my opinion, networking really helpful in our daily life. It makes us easy to connect with other people. Other than that, it benefits us in terms of works. The main thing is that it is very exciting to explore networking. There are too many tools that I do not know. I use it but i do not know the exact name of the tools. It is such a waste if I do not grab this knowledge.
In my opinion, networking really helpful in our daily life. It makes us easy to connect with other people. Other than that, it benefits us in terms of works. The main thing is that it is very exciting to explore networking. There are too many tools that I do not know. I use it but i do not know the exact name of the tools. It is such a waste if I do not grab this knowledge.
No comments:
Post a Comment